Jump To:
Fast Facts
- Operation Duration: 30-60 Minutes
- Hospital Stay: NO
- Approximate Length Of Stay: 1 Week
- Success Rate: About 95%
Lacrimal Duct Surgery
“Lacrimal Duct Surgery”, also known as “Dacryocystorhinostomy” (DCR), is a procedure performed to treat blocked tear ducts (nasolacrimal duct obstruction).
This condition can cause excessive tearing (epiphora), recurrent eye infections, and inflammation of the lacrimal sac (dacryocystitis). The surgery creates a new pathway for tears to drain from the eyes into the nose, bypassing the obstruction.
Indications for Lacrimal Duct Surgery
- Chronic tearing (epiphora)
- Recurrent dacryocystitis (infection of the lacrimal sac)
- Acute dacryocystitis with abscess formation
- Failure of conservative treatments such as probing, dilation, and stenting
Types of Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR)
1. External DCR
- Description: An incision is made on the side of the nose near the inner corner of the eye to access the lacrimal sac and create a new drainage pathway.
- Advantages: Direct access to the lacrimal sac and nasal mucosa, allowing for a high success rate.
- Disadvantages: Visible scar (although usually minimal).
2. Endoscopic DCR
- Description: A minimally invasive procedure using an endoscope inserted through the nasal cavity to create a new drainage pathway.
- Advantages: No external scar, less tissue disruption, and quicker recovery.
- Disadvantages: Requires specialized equipment and expertise.
Procedure Steps
Pre-Surgery Preparation
- Consultation:
- Thorough examination by an ophthalmologist or oculoplastic surgeon.
- Discussion of medical history, symptoms, and previous treatments.
- Diagnostic tests such as dacryocystography or dacryoscintigraphy to confirm the site of obstruction.
- Pre-Operative Instructions:
- Avoiding medications that can increase bleeding (e.g., aspirin, ibuprofen) prior to surgery.
- Fasting if general anesthesia is to be used, although local anesthesia with sedation is also common.
The Surgery Procedure
External DCR
- Anesthesia:
- Local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia.
- Incision:
- A small incision is made on the side of the nose near the inner corner of the eye.
- Bone Removal:
- A small piece of bone between the lacrimal sac and the nasal cavity is removed to create a new drainage passage.
- Creating a New Pathway:
- The lacrimal sac is opened and connected to the nasal mucosa to form a new tear drainage route.
- Stenting:
- Silicone tubes may be inserted to keep the new pathway open during healing.
- Closure:
- The incision is closed with sutures, and a small bandage is applied.
Endoscopic DCR
- Anesthesia:
- General anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation.
- Endoscope Insertion:
- An endoscope is inserted through the nasal cavity.
- Creating a New Pathway:
- The surgeon removes a small piece of bone and creates an opening between the lacrimal sac and the nasal cavity.
- Stenting:
- Silicone tubes may be used to keep the new passage open during healing.
- Completion:
- The endoscope is removed, and the nasal cavity may be packed to control bleeding.
Post-Surgery Care
- Immediate Recovery:
- Mild discomfort, swelling, and bruising are common.
- Use of cold compresses and prescribed medications (antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs) to manage symptoms.
- Post-Operative Instructions:
- Avoiding strenuous activities, nose blowing, and sneezing with an open mouth to prevent disrupting the surgical site.
- Following specific instructions for nasal and eye care.
- Using prescribed eye drops or ointments to prevent infection.
- Follow-Up:
- Regular follow-up visits to monitor healing and remove stents if used.
- Most patients can return to normal activities within 1-2 weeks, with full healing taking a few months.
Potential Risks and Complications
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Scarring
- Failure of the new drainage pathway to remain open
- Granuloma formation (small area of inflammation)
- Adhesions or blockage of the new passage
Benefits of Lacrimal Duct Surgery
- Relief from excessive tearing
- Reduction in recurrent infections and inflammation
- Improved quality of life and comfort
Conclusion
Lacrimal Duct Surgery, specifically “Dacryocystorhinostomy”, is an effective treatment for blocked tear ducts, providing significant relief from symptoms and improving the quality of life. A thorough evaluation and consultation with an experienced ophthalmologist or oculoplastic surgeon are essential to determine the best surgical approach. Proper post-operative care and follow-up are crucial for a successful outcome and minimizing potential complications. SHIFA accompanies you step by step to achieve the best result of your eye surgery.
Compare Before and After Images

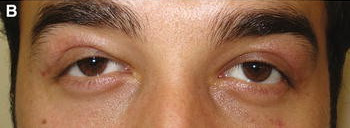
Lacrimal Duct Surgery
Frequently Asked
Questions
Why choose SHIFA for Eye Surgery?
SHIFA Eye Center is equipped with cutting-edge medical technologies that are on par with developed countries. The cleanliness and staff professionalism of Iranian clinics and hospitals are also exceptional. Iran offers the most affordable eye treatments in comparison with other countries.
Does tear Duct Surgery leave a scar?
A major advantage of having an endoscopic DCR is that no incision is made, meaning no scar will form on the face. It is also a less invasive method of surgery, so the recovery is generally both shorter in duration and more manageable.
What age can you get Tear Duct Surgery?
Wait until your baby is 1 year old to see if the blocked tear duct opens on its own. If it doesn’t open, you can decide about the procedure then.
SHIFA's Departments
Related Services
Featured Services

Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
“Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery” (OMFS) is a specialized field of surgery focused on the diagnosis, surgical treatment, and management of
Full Face Thermage
“Thermage” is a non-invasive cosmetic procedure that uses Radiofrequency (RF) energy to tighten and smooth the skin. It is often
Mommy Makeover
A “Mommy Makeover” is a combination of cosmetic surgical procedures designed to restore and improve a woman’s body after pregnancy
Periodontics
“Periodontology”, also known as “Periodontics”, is a specialized branch of dentistry that focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of
Our Blog Articles
- mehdi.mhj@gmail.com
Doccure – Making your clinic painless visit?
Explore the benefits & challenges of virtual healthcare appointments, along with tips for making good...
Read More- mehdi.mhj@gmail.com
Benefits of Consulting With an Online Doctor
Uncover strategies to achieve a harmonious balance between professional and personal well-being....
Read More- mehdi.mhj@gmail.com
5 Great reasons to use an online doctor to choose
Delve into the impact of digital life on mental health & discover practical strategies to...
Read More- mehdi.mhj@gmail.com
What are the benefits of online doctor booking
Explore importance of quality sleep & learn tips to improve your sleep, ensuring raise-up refreshed...
Read More





Comments are closed.